PRP: Platelet Rich Plasma
PRP Scientific Bases
Platelet-rich plasma (PRP), first described in 1998, is a biological product produced by centrifuging blood in a tube containing an anticoagulant. It is a liquid product defined as a suspension of platelets in plasma characterized by a higher platelet concentration than that of the patient’s whole blood. The PRP is intended for autologous use (for each patient himself). A multitude of different PRPs exist according to the preparation protocol, more or less rich in leukocytes, more or less pure, more or less concentrated.
Platelets contain a natural reservoir of growth factors in their alpha granules, which are the active substance in PRP. These growth factors are TGF β (transforming growth factor beta), PDGF (platelet-derived growth factor), IGF1 (insulin-like growth factor), FGF1 (fibroblast growth factor), EGF (epidermal growth factor) and VEGF ( vascular endothelial growth factor).
They are involved in the proliferation and cell differentiation of keratinocytes, fibroblasts, endothelial cells, chondrocytes, smooth muscle cells and myoblasts, and are involved in the healing of cartilage tissue. Platelet alpha granules also contain bioactive molecules such as serotonin, histamine, dopamine, adenosines, calcium, catecholamines, which play a fundamental biological role in the three phases of cartilage repair (inflammation, proliferation, remodeling). Platelet concentrates also have bacteriostatic properties, demonstrated on staphylococcus epidermidis and staphylococcus aureus, thus reducing the risk of microbial contamination of the treated area.
The treatment of traumatic and degenerative pathologies of the osteoarticular system has aroused great interest from surgeons in recent years. In osteoarthritis, the majority of clinical trials and case series involve the treatment of osteoarthritis of the knee, the results of which are promising.
The preparation of PRP requires a blood sample, which is centrifuged to separate the platelet-poor plasma (PPP, 5%) at the surface, the plasma rich in platelet and fibrinogen (PRP, 40%) in the middle, granulocytes and leukocytes at the bottom of the tube (55%). The cell separator increases the concentration of platelets and growth factors in their alpha-granules from 200 to 600%. Depending on the material used and the single or double centrifugation, the composition of the PRP may be variable in terms of platelet concentration and growth factors; it must not contain granulocytes or leucocytes and must not be coagulated.
The use of a local anesthetic before the injection of PRP is contraindicated, it would modify the local pH, however, the quality of PRP is very pH-dependent. The plasma concentrated in platelets is then reinjected into the pathological area. These platelets release growth factors in large numbers, allowing scarring of damaged tissue by stimulating local stem cells, and reducing inflammation and hemorrhage.
Anti-inflammatory drugs should not be used the previous days and the two weeks after the injection of PRP, they may inhibit the action of prostaglandins and thus the stimulating effects of PRP. Local anti-inflammatory treatments should also be avoided. In case of pain, we will use paracetamol.
In practice, how will your PRP session take place?
It will be necessary beforehand to be able to benefit from the treatment of your knee arthritis by an injection of PRP, to fill with the greatest care the questionnaire “KOOS” (Knee injury and Osteoarthritis Outcome Score). It is a question of knowing well the clinical state of your arthritic knee to objectively appreciate the importance of your attack, secondly the importance of the improvement that you will have. This is how you will have to complete this questionnaire in the third month and in the sixth month again.
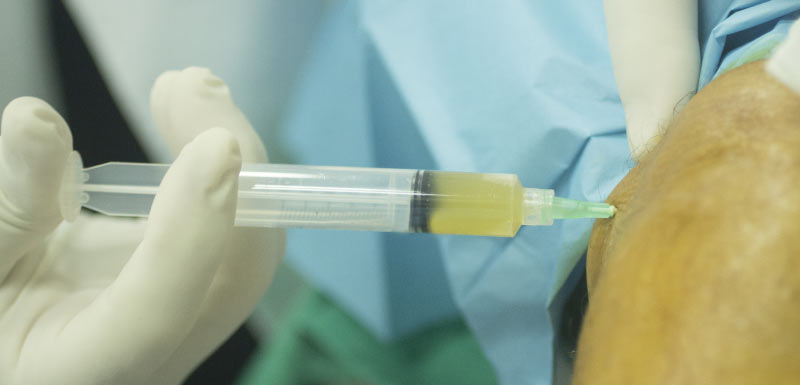
It will be necessary beforehand to be able to benefit from the treatment of your knee arthritis by an injection of PRP, to fill with the greatest care the questionnaire “KOOS” (Knee injury and Osteoarthritis Outcome Score). It is a question of knowing well the clinical state of your arthritic knee to objectively appreciate the importance of your attack, secondly the importance of the improvement that you will have. This is how you will have to complete this questionnaire in the third month and in the sixth month again.

They can also take place at the Clairval Clinic for tendinopathies or meniscopathies.
Finally, they are performed in the operating room either during an intervention on your knee, or for intraosseous injections which can also be a way to medically treat more serious knee arthritis. These procedures are performed in this case under general anesthesia.
